Catalog excerpts

The Properties and Performance of Tensar Uniaxial Geogrids The essential guide to the long-term properties of Tensar Uniaxial Geogrids for use in designing: Bridge abutments Retaining walls Steep embankment slopes Slip repairs
Open the catalog to page 1
Tensar design consultation or workshop www.tensar-international.com 2 How to use this guide This is your essential guide to the long-term properties of Tensar uniaxial polymer geogrids for use in reinforced soil structures. Polymers are not simple elastic materials. Their load-strain behaviour is also affected by time and temperature. These effects are product specific and they lead to a unique design strength for each project and set of conditions. There is a simple conceptual formula: Design strength = Long-term strength factors Long term strength may be defined in terms of rupture...
Open the catalog to page 2
3 Figure 1: Effect of temperature and strain rate on tensile strength of polymer geogrid. Tensile strength All polymer based products are visco-elastic. Their strength and stiffness are affected both by temperature and by rate or duration of loading, as shown on Figure 1. Therefore, it is important that standard methods of tensile testing are used, so that temperature and strain rate are defined. For Tensar uniaxial geogrids, quality control (QC) tensile testing is carried out using the method given in International Standard BS EN ISO 10319:1996. This is a wide width method with specimen...
Open the catalog to page 3
Tensar design consultation or workshop www.tensar-international.com 4 Long-term creep rupture behaviour Due to the visco-elastic nature of polymers, it is not possible to use tensile tests to determine load-strain behaviour for long durations of sustained loading. To do this, a different type of test is used, normally referred to as a creep test. A creep laboratory is shown on Figure 3, where a number of creep tests can be seen in progress. A weight is hung on each specimen, and strain is measured for a standard duration of 10,000 hours. However, many tests are left to run for much longer...
Open the catalog to page 4
5 The long-term deformation behaviour of polymer geogrid is assessed by constructing isochronous load-strain curves. Isochronous data is taken directly from the straintime curves shown on Figures 4a and 4b by reading off the data from the plotted lines at fixed time values. Figure 6 shows isochronous load-strain curves determined in this way for Tensar 120RE at 20ºC, for both 1 month and 120 years duration. For serviceability limit state design to BS8006:1995, isochronous curves are used to find the geogrid load which limits postconstruction strain to: 1% over the period between 1 month and...
Open the catalog to page 5
Tensar design consultation or workshop www.tensar-international.com 6 The trial procedure is illustrated in Figure 9. A layer of fill is placed both below and above the geogrid. The upper layer is compacted to three levels of compaction and then carefully excavated so that the geogrid can be recovered. The geogrid is examined to check for damage. Based on this examination, test specimens are selected from the areas which exhibit the greatest damage. Wide width tensile tests are carried out on these specimens, and the results are compared to tests carried out on control samples. Typical...
Open the catalog to page 6
7 External exposure In most applications geogrid will be buried in soil, so that it will be protected from external environmental conditions. However, at a number of stages during its use, it is likely to be exposed, certainly during handling and installation on site, but also possibly in service. Exposure might be for a relatively long duration, and it is therefore important that the geogrid material is well protected. Some construction specifications and approval certificates provide protection by limiting the allowable duration of exposure, but these requirements are difficult to control...
Open the catalog to page 7
Tensar design consultation or workshop www.tensar-international.com 8 Effects of burial Chemical resistance Buried geogrid will come into contact with soil and ground water, both of which can contain potentially aggressive substances. HDPE is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, and it is inert to all aqueous solutions of acids, alkalis and salts normally found in soils. In addition, it has no known solvents at ambient temperatures. Because of its stability under a wide range of chemical conditions, HDPE is used in many situations where hazardous or aggressive chemicals are present, for...
Open the catalog to page 8
9 Connecting Tensar Uniaxial Geogrids Tensar uniaxial geogrids may be easily connected together on site in the direction of loading using a polymer bodkin joint bar. The bodkin joint provides a full strength connection, so that no reduction factor or partial safety factor is required in designs which incorporate the joint. This versatile connector can be used to: connect main reinforcement to short starters (as shown in Figure 14) use short off-cuts to minimise waste form wrap-around connections in slope construction The unique form and properties of Tensar uniaxial geogrids make them ideal...
Open the catalog to page 9
Tensar design consultation or workshop www.tensar-international.com 10 Mechanical interaction with soil Stabilising soil masses using reinforced soil techniques requires mechanical interaction between geogrid and soil. Interaction can take the form of sliding or pullout. Examples of failure mechanisms which mobilise these two forms of interaction are shown on Figure 16. Sliding between geogrid and soil is defined by a simple coefficient of friction given by: friction coefficient = átanö’ where ö’ = friction angle of the soil á = interaction factor The interaction factor (á) is therefore a...
Open the catalog to page 10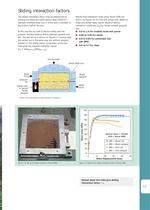
11 Figure 17b: Set up for shear box test on Tensar 80RE. Figure 18: Results from sliding interaction tests on Tensar 40RE. Figure 17a: Cross section of shear box test to measure ás. Sliding interaction factors The sliding interaction factor may be determined by carrying out shear box tests using a large (300mm) specially modified shear box in which grid is clamped to the bottom half of the box. In this way the top half of the box slides over the geogrid, thereby creating sliding between geogrid and soil. The test set-up is shown on Figure 17. Control tests are carried out in the same way,...
Open the catalog to page 11All Tensar International catalogs and technical brochures
-
Tensar HX
1 Pages
-
Road-Technology
12 Pages
-
TensarTech® EcoCrib™
2 Pages
-
TensarTech® SlopeLoc™
2 Pages
-
TensarTech™ slopeloc™
3 Pages
-
Asphalt Reinforcement
10 Pages
-
Tensar_Erosion_Control
12 Pages
-
Tensar Mining Brochure
8 Pages
-
Tensar General Brochure
20 Pages
-
Tensar Architects Brochure
11 Pages
-
TensarTech Plateau Brochure
6 Pages
-
Tensartech TW1 Wall Brochure
6 Pages
-
TensarTech Stratum Brochure
6 Pages
-
TensarTech Ares
2 Pages
-
Tensar Ballast Stabilisation
2 Pages
-
Tensar Wind Energy Brochure
6 Pages
-
Tensar Erosion Control Brochure
12 Pages
-
Tensar GlasstexPatch 880
2 Pages
-
Tensar Mining Brochure
4 Pages
-
Tensar Railway Brochure
12 Pages
-
Tensar Sub ballast Stabilisation
12 Pages
-
Tensar TriAx Geogrid Brochure
12 Pages
-
TensarTech Stratum
6 Pages
-
Tensar Railways
12 Pages
-
Tensar Oil and Gas Brochure
5 Pages
-
TENSAR GEOPIER FOUNDATIONS
8 Pages
-
Tensar Erosion Control
12 Pages
-
Tensar_TriAx_TX
12 Pages
-
Foundations over Piles
6 Pages
-
Basal Reinforcement
6 Pages
-
TensarTech_TW3
6 Pages
-
TensarTech_TW1
6 Pages
-
Tensartech_TR2_System
4 Pages
-
TensarTech_NaturalGreen
6 Pages
-
TensarTech_GreenSlope
6 Pages
-
Tensartech_Geocell_brochure
6 Pages
-
Wind_Energy_Brochure
6 Pages
-
Tensar_Oil_and_gas_brochure
5 Pages
-
Tensar_GlasstexPatch_880
2 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Tensar_Mining_Brochure
5 Pages
-
Tensartech_TW3
6 Pages
-
Tensar_Sales_Leafle
3 Pages
-
New_Architects
11 Pages
-
Tensartech_Green Slope
6 Pages
-
Tensar Basal Reinforcement
8 Pages
-
Tensar Erosion Brochure
2 Pages
-
TriAx brochure 2010
12 Pages
-
Tensar Railways Brochure
12 Pages
-
Tensar General Brochure
20 Pages















































































