
Catalog excerpts

Long Carbon Europe Sections and Merchant Bars Angelina™ beams A new generation of castellated beams
Open the catalog to page 1
The intelligent solution for long spans
Open the catalog to page 2
4. Tolerances of Angelina™ beams 10 5. Angelina™ beams in roofing and metal decking applications 6. Angelina™ beams in composite floor application 7. Stability in fire and fire safety 8. Angelina™ Predesign charts 9. Predesign charts: design examples 10. Angelina™ beams: a solution for sustainable development Technical Advisory & Finishing Your partners
Open the catalog to page 3
1. Introduction The use of Angelina™ beams allows a new architectural expression. Structures are lightened and spans increased, thus open spaces by increased size of column-free floor areas. This flexibility goes together with the functionality of allowing technical installations (pipes and ducts) to pass through the openings. The lightweight appearance of Angelina™ beams, combined with their high strength, stimulates the architects to new structural forms. Progress has now been made on a number of factors that enable the use of Angelina™ beams to be extended: . Manufacturing The...
Open the catalog to page 5
2. Application fields 1. Roofing The use of Angelina™ as roofing elements enables large spans, of about up to 40 meters, to be covered. The competitiveness of the Angelina™ solution is confirmed both by the retention of the functionalities of truss girders and by the reduction of on-site interventions for assembly. Angelina™ beams offer architects attractive and practical solutions in terms of use of space without screening effect. The height of the openings can reach 80 % of the total height of the beam and it is possible to leave only a small distance – required for fabrication – between...
Open the catalog to page 6
Figures 2 and 3: AngelinaTM floor beams 3.1. Renovation In order to preserve the architectural heritage, light and flexible structures based on Angelina™ beams are used to strengthen, reuse and modernize old buildings. 3.2. Beams in car parks There are four reasons for recommending the use of Angelina™ beams for building car parks even if special fire resistance is required: . the traditional spans (15 to 16 m) are within the typical range, . drainage is facilitated by slightly cambered beams, . the openings improve the interior appearance of these structures allowing the natural light...
Open the catalog to page 7
3. Concept – fabrication Angelina™ beams are fabricated in modern installations on the site of ArcelorMittal’s rolling mill for heavy sections at Differdange (Luxembourg). The proximity of these installations limits transport, maximizes responsiveness and contributes to the competitiveness of the manufacturing costs. The patented method used for the fabrication of Angelina™ beams is based on the exclusive use of hot rolled sections. Figure 4: Diagram of the fabrication of an Angelina™ beam Stage 1: flame cutting Stage 2: separation of T-sections A single cut following a specific sinusoidal...
Open the catalog to page 8
1. Choice of size and spacing of openings For a given starting section, there are endless possible combinations of opening sizes and spacings (fig 6). The choice is subject to the following principle. A final adjustment of the openings geometry allows an even more economical fabrication if it enables welding of the first and the last web post without fillings. Figure 6: Definition of an Angelina™ beam Optimization of the height/weight ratio Optimization of the load/weight ratio Starting section (height h) Starting section (height h) Design type 1 Design type 2 Offshore structures Wide-span...
Open the catalog to page 9
2.4 Supporting concentrated loads Local plastic deformation on the transverse diameter of an opening (usually isolated openings close to concentrated loads or at points of maximum stress) can be avoided by stiffeners as described in 2.2 (fig 8). In order to support high shear forces close to the supports or for reasons of fire safety, sometimes it becomes necessary to fill certain openings (fig 7). This is done by inserting discs made of steel plates and welding from both sides. The thickness of the plate and the weld seam are optimized according to the local stresses. Figure 7: Example of...
Open the catalog to page 10
5. Connecting of Angelina™ beams Examples of Angelina™ beams that can be ordered are shown in figure 9. When designing the framework, special care should be given to the positions of the openings in order to avoid unnecessary filling (fig 10). Figure 9: Possibilities for the supply of Angelina™ beams . The first step is to optimize the beam from a structural point of view. . The second step is to adjust the spacing between openings so as Outline sketch of AngelinaTM beams to have a complete web at the ends of the beam. Angelina™ delivered “as fabricated” and overlength Figure 10:...
Open the catalog to page 11
4. Tolerances of Angelina™ beams Angelina™ tolerances Final Angelina™ height: Ht Misalignment of T-sections: T (between axis of upper section and axis of lower section) Spacing: e Distance from first to last opening: B
Open the catalog to page 12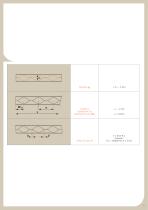
Length: L Distance of 1st opening from end: Wend
Open the catalog to page 13
5. ngelina™ beams in roofing and metal A decking applications The Angelina™ beams used in metal roofs and decks are double symmetrical sections; the upper member and lower member are from the same parent section (fig 12). Figure 12: Make-up of a symmetrical Angelina™ beam Architects and engineers have a large choice of possible opening height and spacings. From these two values, the starting section can be determined and the final height of the Angelina™ beam can be deduced. The process can also be reversed: from a required final height and opening dimensions, the designer can easily...
Open the catalog to page 14
For standard roof projects, the beams can have a slenderness (span/height ration of the beam) from 20 to 40 depending on the support conditions. An intermediate value of 30 can be used as a starting point for secondary beams and for the fixed beams of frames (fig 14). The choice of the height and the spacing of the openings is normally guided by architectural requirements (transparency and light effect) and functional requirements (passage of services through the openings). However, there are geometric limits to be respected for good mechanical behaviour of the Angelina™ beam. These limits...
Open the catalog to page 15All ARCELORMITTAL Long catalogs and technical brochures
-
Long Products
180 Pages
-
Slim-Floor
40 Pages
-
ACB® and Angelina® beams
64 Pages
-
Bridges With rolled sections
52 Pages
-
Bars and Rods
36 Pages
-
Stainless steel in construction
68 Pages
-
Arval Sunstyl
16 Pages
-
Pflaum & Söhne Bausysteme GmbH
72 Pages
-
Arval Colorissime
10 Pages
-
Steel Sheet Piling
56 Pages
-
Beam Finishing
8 Pages
-
ACB - Cellular Beams
48 Pages
-
RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
68 Pages
-
Safety Barriers
12 Pages
-
Pfl aum & Söhne Bausysteme GmbH
72 Pages
-
Aluzinc® in Building
8 Pages
-
Colorissime
10 Pages
-
Form Tie Bars
2 Pages
-
ExpandedMetal
24 Pages
-
CARRIL / RAIL
28 Pages
-
AMCRPS
52 Pages
-
Sections and Merchant Bars
244 Pages
-
arival system by arcelormittal
80 Pages
-
ArcelorMittal Piling Handbook
368 Pages
-
Sunstyl
16 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Material Selection Guide
23 Pages
-
Floor systems guide
96 Pages










































